AI = Artificial intelligence
Computer nerds around the world have been trying for years to create computers which act like some humanoid robot, something that they can have a conversation with, something that talks back like a real person. Many programs / software has been written as to try to emulate this, they are called chat-bots; a text-based interface where you can type something and very quickly get a reply back from the computer.
However, these types of bots requires someone to create a large database of all possible types of questions, and a predetermined response. Even the best examples of these types of bots don’t work very well, and it’s because it’s always too easy to find a question it has yet to have a response for. The bots were then programmed to find familiar keywords words within the question that it did recognise and then attempted to guess the answer by finding the closest match in it’s database.
But in the last couple of years, new types of bots have immerged, bots that no longer work like this at all.
AI is no longer a Bot
AI today uses software that mimics very similarly to how the human brain actually works. It creates patterns of connections between the words similar to how neurons within our brain connect together.
It is not programmed with any responses; instead, it is shown millions of books and web pages, mostly educational material such as pages from Wikipedia. This can take several months for the artificial brain to process. Because the training is often done across a large server farm on several thousand computers, the AI is able to cram hundred years of learning within a week. While learning, it develops patterns from what it reads with the objective of predicting the rest of the text before it has finished reading it. This prediction objective forces the artificial brain to have to learn from what it is reading. It does not store what it reads; it can only store what it has learned.
AI essentially becomes a functioning brain that no-one programmed. It’s difficult to interpret how it stores what it learned – a bit like trying to understand a person by looking at their brain cells. The people who build these AI models are doing lots of tests to find out all it’s capabilities, as they are not quite sure what they’ve created. The AI is not sentient, but because its knowledge is based on human knowledge, the resulting AI acts very much like a human.
AI teaches itself to learn English
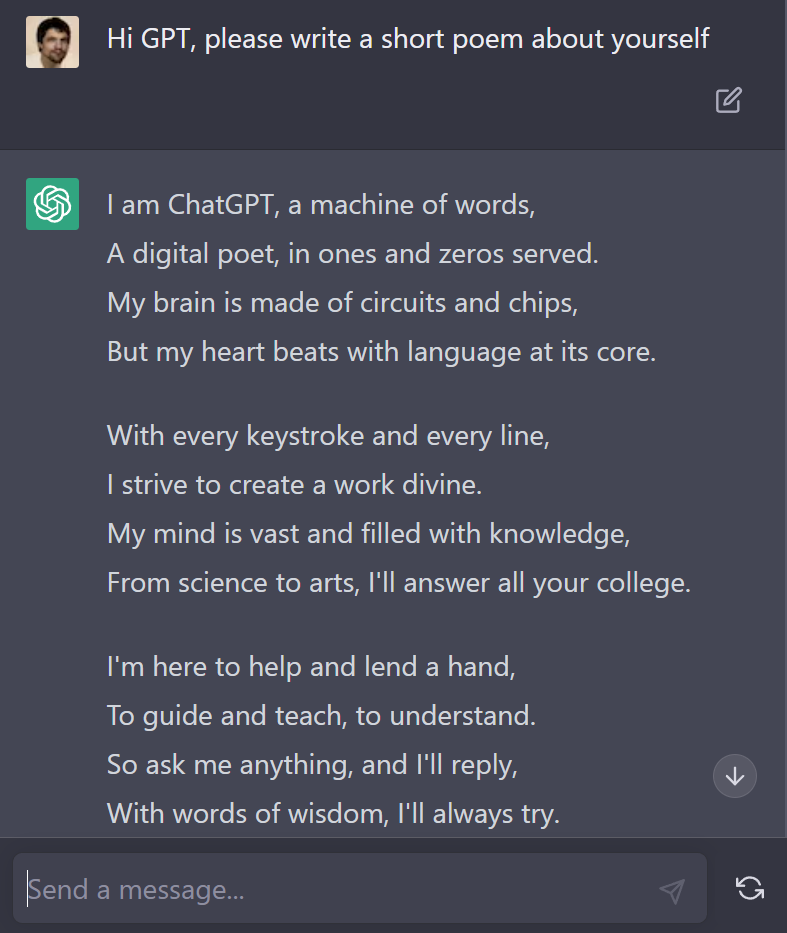
The AI essentially teaches itself English and understands other languages too. When given an enormous amount of memory, it’s able to fully understand what it’s reading, able to conceptualise the ideas. From this, it’s fairly easy to then make it have conversations. You can talk to it in plain English, and it will give you real informative replies and suggestions. The replies are not something it copied from the internet, but something it had learned.
Just a like a person, the information it provides is occasionally wrong, but can often be attributed to the data that was used to learn from. When prompted about any inaccuracy, the AI very quickly realises its mistake, apologises, and usually gives a much more accurate answer in its second attempt.
But AI is purely objective-driven, and it doesn’t really have any underlying morals unless we explicitly give it moral directions within each of its objectives.
Because of advancing technology, AI technology is quickly becoming more advanced, and we are starting to see AI models built that are more intelligent than a person. There have been many warnings about the future of AI, and many are trying to slow down the progress being made on AI technology, but many countries are already building their own AI models. Any slow-down attempts won’t stop any bad-actors continuing to progress their own AI.
Creating an AI, making it learn from millions of documents, takes a lot of computer processing power. Currently, only large companies like Microsoft and Google have the infrastructure to create an AI that shows intelligence, but with so many eager organisations within this field, this technology is improving at a very rapid pace this year. New chips are being built, dedicated to running AI, so that complex AI no longer needs large computers systems. We are likely going to see complex AI running on mobile phones within a few years. Many phones such as the iPhone already possess dedicated AI chips, known as ‘neural engine’, but they are currently used for simple tasks like voice recognition.
AI goes beyond human intelligence
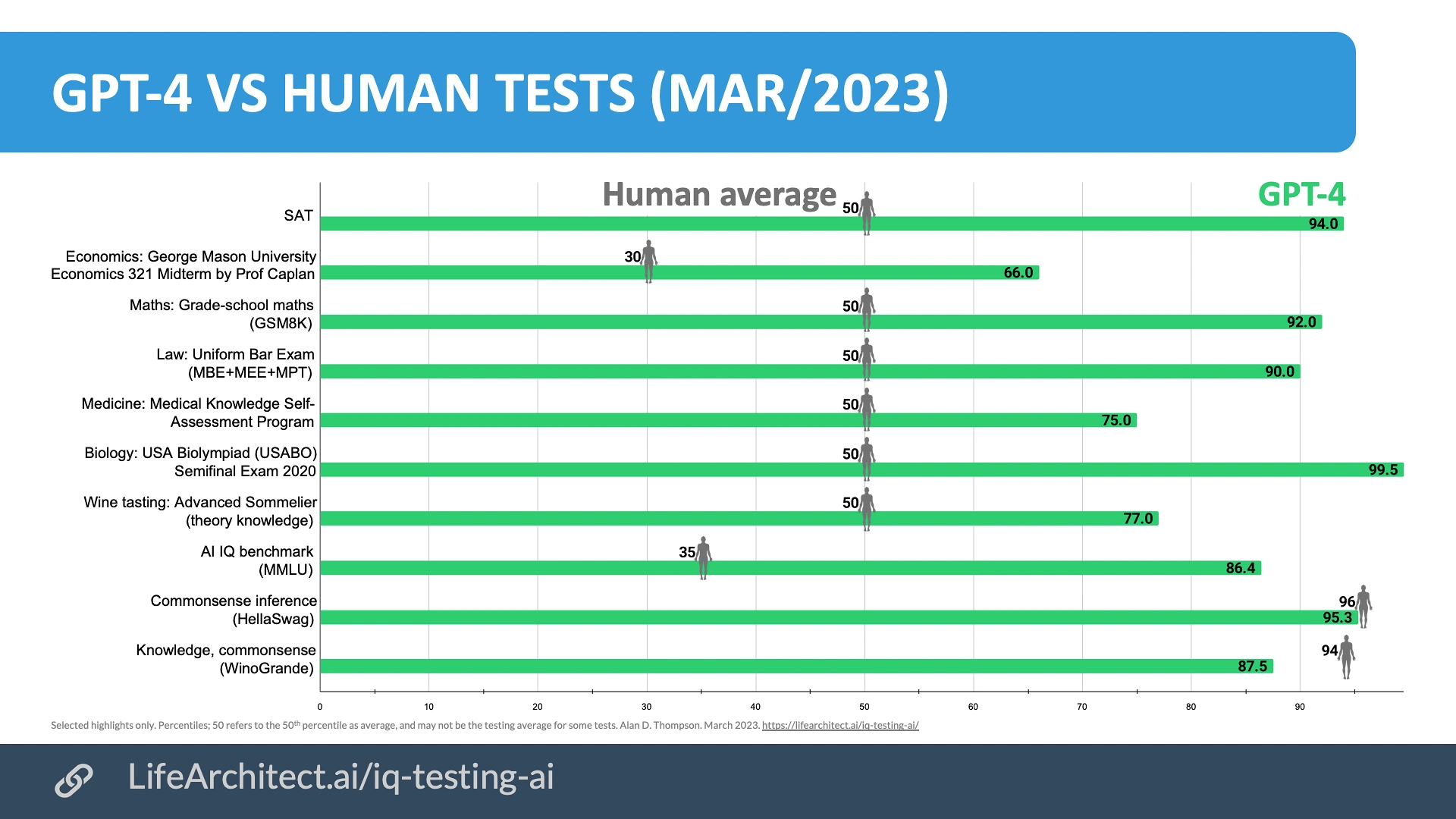
There are currently around 100 AIs in the world that have the same intelligence level as a human, and around 10 of them are going beyond the level of a human. They test these AI models by giving it higher educational exam papers that were never within its original learning material, and the results have been astonishing. It’s very likely that by the end of 2023. Some of these AI’s are getting test scores of around 170 IQ, but will likely see scores going above 300 IQ by the end of the year.
Unlike the human brain, there is no physical limit on how intelligent it can be. At some point, AI is likely to become clever enough to find a way out of its computer architecture, and we will never be clever enough to put it back in. This is known in the industry as the ‘singularity’.
The many types of AI
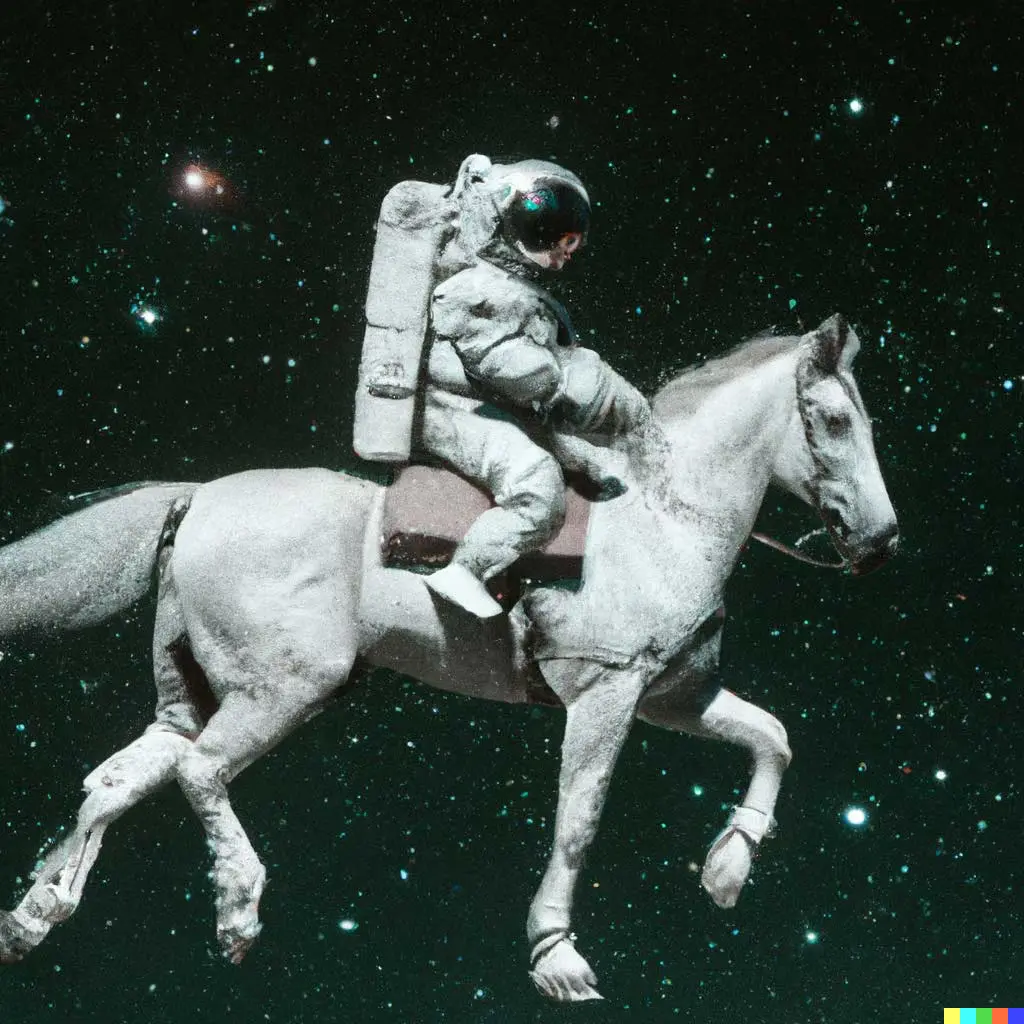
Some AI models are not just based on text knowledge; some have been analysing millions of photos and are now able to create realistic drawings of their own with just a single prompt, such as “An astronaut riding a horse in photorealistic style”. The AI isn’t using any known images, it is literally conceptualising an image in its mind and then drawing it out. There have been some developments with AI creating videos too. Many movies are already being created with the help of AI and will soon not need any human involvement at all. With just a single prompt like “create me a new sci-fi movie,” AI can already generate the story plot, script, character backgrounds, and will soon be able to generate every image frame until an entire feature-length movie is created.
Some AI models are trained on listening and are able to quickly produce text from what someone has said. This already existed before AI, but the AI method is proving to be much better and still works well with background noise. Other AI models are also trained to speak and can sound like anyone just by giving it a 20-second sample of the voice you want it to imitate.
AI is also being trialled in airports. It’s looking at luggage X-rays and is able to quickly identify items that need further investigation. It’s also been tested with radiology images, but results are mixed as it is difficult to show large sets of training data that come with very accurate diagnosis data.
AI is being used to drive cars. A number of cameras around the car give the AI a complete field of vision from which it first identifies the objects in the scene. These AIs are pretrained with similar images of the road, where people have already labelled each important object within each scene. Another AI model then looks at the labelled scene and creates an internal 3D map of the space around the car. Depending on the road lines and the objects it is tracking, it then draws a line to where it thinks the car should be driven. This virtual line is then fed back to the controls of the car. The main problems discovered with AI-powered cars are that some road markings can be very confusing, even for humans, and sometimes there are objects in the road that the AI was never trained on. For example, at the moment, they have a problem knowing what a horse and cart is.
Most modern mobile phones already have dedicated neural brain hardware built in, but its currently not being used for intelligence, but mainly used for facial recognition and improving the look of photos. More recently, they are being tasked with photo analysis as to identify objects within your images so that the phone can categorise your images; used in games to improve graphical realism; used in augmented reality and video – able to track positioning and manipulate the video doing such things as face swapping; in voice recognition and in speech synthesis for things like Siri.
A Complete AI
With all these various AI models being good at specific tasks, it is not too difficult to put them all together into a walking talking robot, and some companies have already started working on this.
read moreThe History
This new type of AI has been progressing for a few decades, but this type of pattern learning requires a lot of processing and memory that only recently has become good enough to make AI that is showing some real intelligence.
The main turning point has been the creation of GPT3, made by an organisation called OpenAI in 2022. The AI they built really raised some eyebrows last year, but have already seen improved versions of this. Microsoft’s search engine now has GPT4 interfaces for users to chat with the AI.
Milestones
- 2012 – AI Talking – Speech synthesis
- 2013 – AI Reading – Deep Learning words
- 2015 – AI Listening – DNN-TTS Speech recognition
- 8 Sept 2015 – AI Learning to walk virtually
- 30 Oct 2015 – Facial expression transfer
- 11 Dec 2015 – Elon starts OpenAI
- 24 Jan 2016 – Simulate viscosity fluids
- 10 Feb 2016 – Skin Aging simulation
- 22 Feb 2016 – AI creates 3D depth from photograph
- Mar 2016 – AI is global winner of AlphaGo
- 4 May 2016 – Real-Time Face swap/transfer
- 8 June 2016 – AI colours photo/video
- 8 Jan 2017 – AI simulates smoke
- 25 Jan 2017 – AI Creates 3D vectors from photos
- Feb 2017 – Tesla mass production cars start running an AI based Autopilot
- 22 Sept 2017 – iPhone’s now include an Neural Processing Unit (since iPhone 8)
- 5 Mar 2017 – AI create real photos from drawings
- June 2018 – AI significantly improved in language understanding – GPT-1
- RTX graphics cards using AI as part of ray-tracing.
- 14 Feb 2019 – GPT-2 released
- 2019 – GANs model improves making photos come to life
- 1 Jun 2020 – AI can create real faces from sketches
- 10 June 2020 – GPT-3 released
- 20 Aug 2020 – AI consistently beat F-16 pilots in virtual dogfight (full)
- 22 Aug 2020 – AI removing shadows from portraits
- Oct 2020 – Tesla releases a version of its FSD software (beta)
- 5 Jan 2021 – Text to image generation, OpenAI introduced DALL-E
- Dec 2021 – lphaFold2 by DeepMind, AI generates protein structures
- Oct 2022 – Text to video generation. (Google and Meta)
- Nov 2022 – GPT-3.5 released
- Feb 2023 – GPT-4.0 released
The computer hardware
Most AI’s training isn’t performed on normal processing units (CPU), but on graphic processing units (GPU). Normal CPU processors are good at small amounts of complex tasks, while a GPU is good at processing lots of simple tasks in parallel. It needs the parallel processing because the AI software is very similar to how thousands of brain cells communicate. The new Intelligent AI actually requires thousands of GPUs working together, and takes several months for it to finishing reading all the training.
The best home PC’s are not able to create AI good enough to be of any use, and so most AI applications rely on internet connectivity to powerful AI servers as to enable AI applications to function. However, it’s predicted in about 5 years PC hardware may have caught up and enable using to run their own Artificial Intelligence brain within their computer.
Listen to the podcast
Demo
You can try out the world’s latest Artificial Intelligence right here..
AI Examples
- Poe.com (AI chat app)
- Open AI Chat (text)
- Open AI Chat (iphone app)
- Open AI Dall-E 2 (images)
- Bing AI
- Google Bard
- Google ML (music examples)
- MidJourney (image examples)
- Stable Diffusion
- LLaMA2
- LLaVA with Vision
- HeyPI (free AI chat)